Also in this category
View more in Remote WorkRemote Work
Work-from-Home Requires Exceptional Users’ Experiences, not just Connectivity
Updated on July 12, 2023
By Ray Mota with ACG Research

Work-from-home (WFH) for many employees became the operating standard during Covid-19, but now as the pandemic recedes and workers are gradually returning to the office, it’s time to reflect and analyze on how efficient and productive WFH was and explore a more efficient technology for successful WFH experiences.
In many cases, WFH results in a win-win situation for employees and employers. For example, one benefit is sparing employees from commuting, giving them more time to focus on work for longer each day. Another benefit is attending meetings on time and transitioning quickly between them or having fewer meetings. With video and audio conference calls workers can connect quickly and easily. Participants can share documents and comments through messaging or onscreen. Ultimately, these types of meetings are often shorter than in-person meetings because there are fewer interruptions, and socializing tends to be minimal. WFH provides employees with more unencumbered time to be productive. Employers save on the operational expenses of running the physical offices.
The success of WFH has convinced many employers to accept WFH and are allowing employees to continue working from home. This movement requires that employers address how to make the experience of WFH better. To do this they must adopt improved technologies that are available today, such as wireless WAN. Before we delve into the newer technology, let’s look at the problems faced by WFH users.
Beyond connectivity
Because no one anticipated the extent to which Covid would affect individuals and businesses, the transition to WFH was abrupt and without preparation. The focus was on connectivity and not users’ experiences. Now with WFH firmly in place in many organizations, employees want and need a work experience without latency, without jitter and bandwidth issues and with better video quality. They and their employers want QoS.
A better wireless experience for WFH users
We live in a wireless-first world, connecting homes and offices quickly and effortlessly. Cellular operators have enabled this movement by offering unlimited data plans at flat fees, speed with 5G, and decreasing prices. With wireless being the primary connectivity medium, how can providers make the wireless experience better so that WFH has improved QoS?
Wireless WAN is the new WAN
The usual way employees connect to the office is through their home WI-FI using a single, shared WI-FI with all family members. The current WI-FI networks have no way of prioritizing the WFH traffic from the traffic of other users, for example, those watching Netflix or running other streaming media.
Wireless WAN is an innovative and promising technology that can address these problems by extending corporate WAN seamlessly to the home. The CPE builds a secure tunnel back to the corporate data center and at the same time broadcasts the corporate SSID in the home. The corporate traffic is placed in a separate corporate WI-FI, providing priority to the WFH user over other home users. At the same time, the home users break out directly to the internet without passing the traffic to the corporate data center.
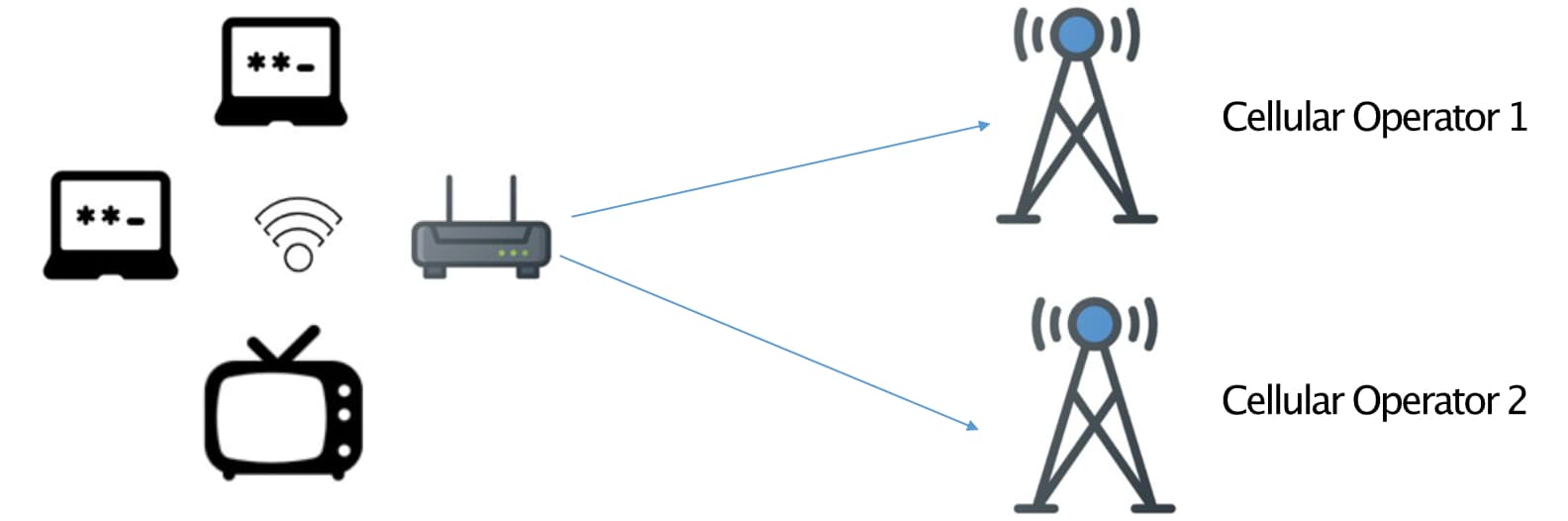
Wireless WAN provides lightweight, secure, and resilient WAN
Although QoS is important, conveniently connecting to corporate networks is essential. With wireless WAN the user does not need to run a VPN client as corporate SSID is directly available. The job of building the secure tunnel back to the data center is offloaded to the CPE, thus the home user does not need to dial a VPN connection. The Wireless WAN has made the VPN redundant.
Wireless WAN can also offer enterprise security at home through the use of application-aware firewalls, threat management capabilities, and cloud security options to securely connect from the traffic source to the edge.
With the option of dual SIMs from different providers and a wired WAN option, the CPE can fall back to redundant second transport to provide resiliency (cellular or wired) should there be any issue on the primary wireless WAN.
Inseego provides wireless WAN
Wireless WAN is available today from vendors such as Inseego, which has differentiated itself by holding vital patents for antenna designs, thermal performance, and quick response algorithms. The wireless WAN benefits for enterprises are straightforward: Providing a better WFH user experience to their employees with a secure and redundant WAN through multiple cellular operators to enable efficiency and productivity. They also want to extend connectivity to their new branches quickly. Operators can tap into the “user-centric” WFH market and business opportunities as well as enable enterprises to connect the remote branches by providing a managed service. For both operators and enterprises wireless WAN is an opportunity to enable QoS WFH users and providing more than just connectivity while differentiating themselves in the market.
Talk to our experts!
Set your customers or business up with the fastest, easiest, most reliable fixed wireless solutions.
